In the fast-paced and interconnected global marketplace, businesses rely heavily on suppliers to maintain the smooth flow of goods and services. However, managing suppliers effectively goes beyond ensuring timely delivery and cost-efficiency. It demands strict adherence to compliance regulations, industry standards, and ethical practices, making supplier compliance a critical aspect of supplier management. This article delves into the importance of supplier compliance in global industries, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices for businesses to enhance their supplier compliance strategies.
Understanding Supplier Compliance
Supplier compliance refers to the ability of suppliers to meet the legal, regulatory, and ethical requirements imposed by the buyer, industry standards, and governing bodies. Compliance covers a wide range of areas, including environmental regulations, labor laws, product safety, cybersecurity, and data protection. It is essential in industries such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, food and beverage, and electronics, where even minor compliance failures can result in severe financial and reputational damage.
Global supply chains are complex, often spanning multiple countries with differing regulations and compliance requirements. As such, ensuring that every supplier, regardless of location, complies with these regulations is vital for minimizing risks and maintaining business continuity.
Role of Supplier Compliance in Supplier Management
Supplier management involves evaluating, selecting, and monitoring suppliers to ensure they meet the company’s quality, cost, and service standards. Compliance adds another layer of responsibility to supplier management, as businesses must ensure that suppliers also adhere to regulatory and ethical standards. A robust supplier compliance program helps companies:
- Mitigate Risks: Mitigating risks through supplier compliance ensures that suppliers comply with quality and safety standards, significantly lowering the likelihood of product defects, contamination, and costly recalls that could impact consumer safety and brand reputation.
- Ensure Quality and Safety: Ensuring that suppliers comply with quality and safety standards is essential in industries where product defects can harm consumers, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
- Evade Regulatory Scrutiny: Adhering to compliance standards minimizes the risk of legal complications by ensuring that both national and international regulations are met, protecting the business from potential fines and sanctions.
- Reputation Boost: Consistently sourcing safe and high-quality products strengthens public trust and enhances the company’s reputation, positioning it as a reliable and responsible brand in the marketplace. Companies that prioritize supplier compliance are more likely to build trust with consumers, investors, and stakeholders.
- Operational Continuity: Ensuring supplier compliance helps maintain a stable and efficient supply chain, reducing disruptions and delays, which supports uninterrupted operations and business growth.
Importance of Supplier Compliance in Global Industries
⇒ Regulatory Landscape
Global industries face a labyrinth of regulatory frameworks that vary across borders. For example, in the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict data privacy rules, whereas U.S. businesses might need to adhere to environmental regulations like the Clean Air Act or industry-specific rules like the FDA’s food safety requirements. Ensuring compliance with such regulations is challenging, but non-compliance can lead to severe legal consequences, including fines, sanctions, and operational shutdowns.
Furthermore, governments are increasingly holding businesses accountable for the actions of their suppliers, pushing companies to implement rigorous supplier compliance programs to avoid costly penalties. Global companies must monitor their supply chains for human rights violations, environmental breaches, and unethical labor practices, particularly in regions where enforcement may be lax.
⇒ Consumer Demand for Ethical Practices
Consumers today are more informed and demand transparency and accountability from the brands they support. There is a growing expectation for companies to source materials and services ethically, respecting environmental sustainability and human rights. Companies that fail to ensure supplier compliance with these ethical standards may face public backlash, leading to a loss of trust and customer loyalty.
Businesses are increasingly investing in supplier compliance programs that emphasize responsible sourcing and ethical practices, often using third-party audits and certifications to verify compliance.
⇒ Supply Chain Transparency and Accountability
As supply chains become more globalized and complex, transparency is a significant challenge. Businesses need visibility into every tier of their supply chain to ensure compliance with regulations, quality standards, and ethical practices. However, maintaining oversight of suppliers, subcontractors, and third-party vendors in distant regions can be challenging without the right tools and strategies.
Technology has played a critical role in enhancing supplier compliance by providing real-time data and visibility across the supply chain. Supplier management software with compliance tracking capabilities allows businesses to monitor supplier performance, assess compliance risk, and ensure that corrective actions are taken when necessary.
Challenges in Achieving Supplier Compliance
While supplier compliance is essential, it is not without challenges. Some common obstacles include:
- Diverse Regulatory Requirements: Navigating the myriad of regulations across different countries can be overwhelming for companies. A lack of harmonized global standards means that businesses must invest significant resources to stay compliant in each market.
- Supplier Resistance or Inadequate Resources: Smaller suppliers may lack the financial or technical resources to meet stringent compliance requirements. In some cases, suppliers may be unwilling to invest in the necessary changes to adhere to regulations, particularly if they do not perceive the same level of enforcement in their local market.
- Lack of Transparency: The deeper tiers of the supply chain (e.g., sub-suppliers) often lack transparency, making it difficult for businesses to assess compliance. Companies may struggle to obtain accurate information from their suppliers or lack the necessary tools to track compliance across all tiers.
- Geopolitical and Economic Factors: Political instability, economic fluctuations, and changes in trade policies can impact supplier compliance. A supplier that once met regulatory requirements may become non-compliant due to shifting legal landscapes or operational difficulties.
Best Practices for Managing Supplier Compliance
To ensure effective supplier compliance, global industries should adopt key strategies as given below:
A. Establish Clear Compliance Requirements
Businesses should define and communicate their compliance expectations to suppliers early in the relationship. This includes outlining specific legal, regulatory, and ethical standards that suppliers must meet. Clear contracts, supplier codes of conduct, and compliance checklists can help ensure that suppliers understand their obligations.
B. Conduct Supplier Audits and Assessments
Supplier audits are essential for verifying compliance with legal and ethical standards. Regularly scheduled audits, both internal and through third-party auditors, provide visibility into supplier practices and help identify any areas of non-compliance. Businesses should assess supplier compliance risks at the outset of the relationship, factoring in the supplier’s location, industry, and past compliance history.
C. Leverage Technology for Compliance Monitoring
Supplier management software and compliance tools can help businesses track supplier performance and compliance in real time. These platforms enable companies to automate document management, track certifications, and monitor regulatory updates. Blockchain technology is also emerging as a tool for ensuring supply chain transparency, allowing companies to trace products and materials back to their source.
D. Foster Collaboration and Support
Instead of taking a punitive approach, businesses should collaborate with suppliers to improve compliance. This may involve offering training, resources, or financial assistance to help suppliers meet requirements. Building long-term partnerships based on mutual trust and transparency encourages suppliers to prioritize compliance and ethical practices.
E. Implement a Strong Risk Management Strategy
Supplier compliance is closely tied to risk management. Businesses should regularly assess the compliance risks associated with each supplier and implement strategies to mitigate those risks. This includes diversifying the supplier base, creating contingency plans, and staying informed about regulatory changes in key markets.
In the global business environment, supplier compliance is a critical element of effective supplier management. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards is essential for minimizing risks, maintaining product quality, and protecting brand reputation. While challenges such as regulatory complexity and supply chain transparency persist, businesses can overcome these obstacles by adopting best practices such as clear compliance requirements, regular audits, and leveraging technology for compliance monitoring. Ultimately, a proactive approach to supplier compliance strengthens supply chains, safeguards business continuity, and ensures sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive global market.
How Smart Supplier Can Be Your One-Stop Solution to Ensuring Supplier Compliance
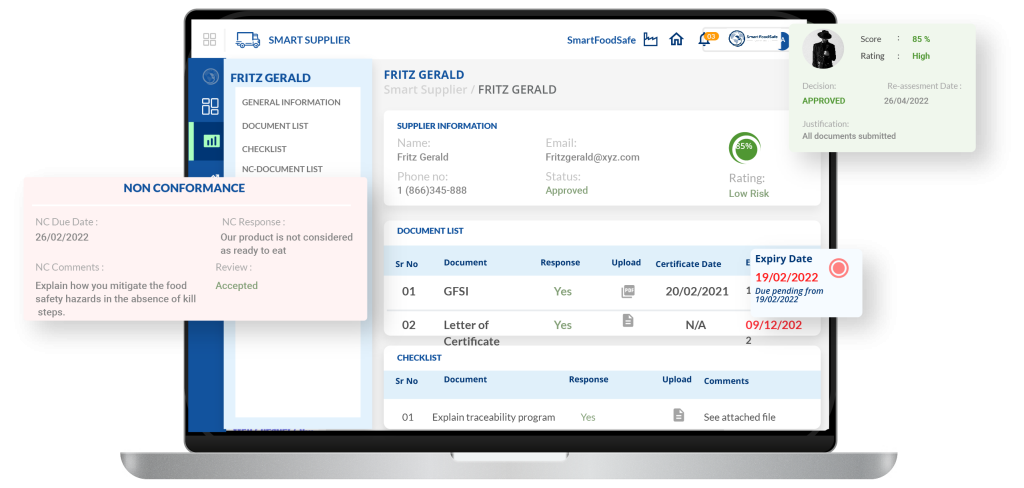
Smart Supplier comes ready with a well-built suite of features to take the supplier management process to the next level, with a primary focus on assisting businesses to achieve supplier compliance through its digital platform. Let’s see how Smart Supplier makes it happen:
End-to-end Supplier Management – Streamlines and automates supplier compliance across regulatory and industry standards, managing the entire supplier lifecycle—from onboarding to reassessment and delisting—while adapting to evolving business needs.
Risk-Based Supplier Assessment – Evaluates suppliers through risk-based assessments to identify, monitor, and mitigate vendor risks, ensuring alignment with business objectives and automating risk-based approval processes for faster, more transparent outcomes.
Supplier Document Management – A centralized platform for collecting, storing, and managing supplier documents such as contracts, certificates, and invoices, improving communication to ensure compliance.
Real-Time Supplier Screening & Alerts – Proactively screen suppliers in real-time and continuously monitor risk and compliance statuses, with alerts and notifications for stakeholders to enable timely responses and risk mitigation.
Performance Tracking & Decision-Making – Monitors supplier performance with real-time visibility into metrics like quality, delivery schedules, and compliance, using customizable checklists and supplier scores for data-driven decisions on requalification or disqualification.
Non-Compliance & Corrective Action Management – Tracks and manages non-compliance issues, facilitating the resolution of supplier non-adherence to both regulatory and internal standards through the platform’s non-compliance management and real-time updates.
Comprehensive Dashboard & Reporting – Offers an exhaustive dashboard for complete visibility into supplier KPIs and performance metrics, enabling users to generate customizable reports and track supplier relationships, engagement, and due diligence efficiently.